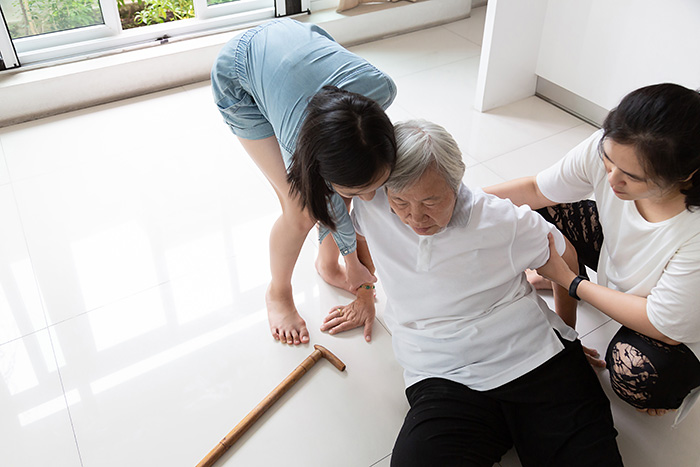
They say ‘Home is the safest place to be’, but is this true? Do you know that even the home can be a dangerous place to live in? Based on WHO (World Health Organization) statistics, an estimated 424,000 fatal falls occur every year in homes. Falls can cause serious injuries such as bone fractures or head injuries. This shows the importance of preventing such unwanted accidents at home. For patients who had experienced falls before, it is even more important to prevent a fall again because it could further deteriorate their health condition.
Most falls are caused by a combination of risk factors. The below are some risk factors that can make one more susceptible to falls and what you can do to prevent falls:
Risk factor 1: Age
Age is the highest risk factor for falls. Statistics have shown that adults over 65 years of age have the highest number of fatal falls. This could be due to several reasons such as poor balance, muscle weakness, low bone density and poor vision.
How to prevent: There isn’t a way to prevent ageing, but you can take supplements such as calcium and vitamin D to help your bone and muscle health.
- Calcium helps to strengthen the bones and may be given together with vitamin D for optimal calcium absorption.
- Vitamin D can also help to improve muscle strength.
- Glucosamine helps to maintain the cartilage, leading to healthier joints and it is frequently used in people who suffer from osteoarthritis (pain in the joints).
- Good vision is crucial to navigate stairs, curbs and avoiding obstacles. It is important to have your eyes checked at least once a year and update your eyeglasses if needed.
Risk factor 2: Concomitant medication use
There are certain medications such as antihistamines indicated for allergies that can have side effects like drowsiness and affecting a person’s mental alertness. Other medications such as anti-psychotics and anti-depressants can also affect mental alertness. High blood pressure medication might also cause dizziness as a side effect.
How to prevent:
- Always consult your doctor or pharmacist on the side effects of the medications which you are taking. You can also discuss and review your medication with your healthcare provider to optimize the medication used to treat your condition.
- Avoid intake of alcohol because it adversely interacts with most medications. Alcohol may intensify medication side effects such as drowsiness which may interfere with your concentration and lead to fall.
Risk factor 3: Lack of exercise
Do you know the benefits of regular exercise? Firstly, it helps in weight management. Secondly, it helps to decrease risk of having cardio diseases. Thirdly, it helps to improve muscle strength and overall helps in improving mental alertness and energy levels. Exercise can help in fall prevention because having more strength in muscles means a lower risk of falling due to weakness in limbs. Improved mental alertness indicates that you are more aware and careful of your surroundings.
How to prevent:
- Exercise consisting of strength, balance, flexibility or endurance can help to prevent falls.
- Specific exercises such as Tai Chi, has been proven to make your legs stronger and improve your balance.
- It is recommended to include at least 60 minutes of fall prevention exercises twice a week.
Risk factor 4: Environment factors
Environmental factors include wet floors, poor lighting, and objects left on the floor which can contribute to falling incidents at home. These risk factors should be identified and corrected in order to prevent falls.
How to prevent:
- For bathrooms: Install grab bars inside and outside shower and next to the toilet. Leave the door open after a shower to let the water on the floor dry quicker. You can also use anti-slip mats or slip resistant flooring on the floor to prevent slipping.
- For living rooms: Use light bulbs that are bright enough and if possible, use a power saving light bulb to conserve energy as well. Always ensure that there aren’t any objects left lying around on the floor so that you won’t trip over it.
- For bedrooms: Place a lamp beside your bed so that if needed, you can easily reach and switch on the lamp to see more clearly in the dark. Alternatively, you can also install a night light. Remove clutter that can be tripped over, there should be minimal things in your room to prevent bumping into things easily.
- Others (footwear): Wear well-fitting shoes with low heeled, a slip resistant soles, and a large contact area to reduce falls.
By identifying the risk factors and being aware of the falls prevention approach, you can help to reduce the risk of falls at home. Ultimately, preventing falls can help to improve the quality of life of the patients and their family, as well as to avoid any unnecessary medical costs and hospitalization for fall-related injuries. Hence, families with elderly or patients who are prone to fall are encouraged to take these falls prevention measures.
Reference
- Health Promotion Board (2015). Falls Prevention Among Older Adults Living in The Community. Singapore.
- World Health Organization (2007). WHO Global Report on Falls Prevention in Older Age. Geneva.
- World Health Organization (2018). Falls. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/